Titanium dental implants are considered the gold standard in restorative dentistry, offering patients a reliable, durable, and aesthetically satisfying solution for missing teeth. With decades of clinical success, titanium implants provide long-term functionality, bone preservation, and natural appearance, making them a preferred choice for both anterior and posterior restorations. This extensive guide explores titanium implants, their clinical advantages, the detailed manufacturing process, surgical procedures, patient suitability, and post-operative care to ensure optimal outcomes.
Understanding Titanium Dental Implants
Titanium implants are made from medical-grade titanium, a material known for its high strength, biocompatibility, and ability to integrate with bone tissue. The unique properties of titanium allow for osseointegration, a process where the implant fuses with the jawbone, providing a stable foundation for crowns, bridges, or overdentures. Key features include:
Biocompatibility: Promotes healthy bone and soft tissue integration.
High Mechanical Strength: Withstands chewing forces and long-term wear.
Corrosion Resistance: Maintains structural integrity over decades.
Versatility: Suitable for single-tooth replacements, full arches, and complex prosthetics.
Proven Longevity: Long-term studies demonstrate success rates above 95%.
Advantages of Titanium Dental Implants
Titanium implants offer a combination of clinical reliability and patient-focused benefits:
Durable and Long-Lasting: Capable of withstanding daily masticatory forces for decades.
Bone Preservation: Stimulates the jawbone, preventing bone resorption that occurs with tooth loss.
Predictable Outcomes: High success rates due to extensive clinical research and established surgical protocols.
Aesthetic Flexibility: Can be combined with ceramic or zirconia crowns for a natural tooth appearance.
Functional Restoration: Restores chewing efficiency, speech, and overall oral health.
The Titanium Implant Manufacturing Process
Titanium implants are produced with meticulous attention to precision, surface quality, and structural integrity.
1. Material Selection
High-purity commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) or titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V) are used. These materials are chosen for their strength, biocompatibility, and resistance to corrosion. The selection ensures implants can withstand long-term functional and mechanical stress.
2. Shaping and Machining
Using advanced CNC machining and computer-aided design (CAD/CAM) technologies, titanium rods are shaped into precise implant geometries. Thread patterns, length, and diameter are customized to:
Maximize bone-implant contact.
Ensure primary stability during insertion.
Allow for compatibility with abutments and prosthetic components.
3. Surface Treatment for Osseointegration
Titanium implants undergo specialized surface treatments to enhance bone integration:
Sandblasting: Creates micro-roughness for bone attachment.
Acid Etching: Optimizes surface texture for faster healing.
Anodization or Plasma Spraying: Enhances surface energy, promoting osteoblast attachment.
4. Quality Control and Sterilization
Before clinical use, each implant undergoes:
Dimensional Accuracy Verification: Ensures correct threading and fit.
Mechanical Stress Testing: Confirms load-bearing capacity.
Surface Analysis: Evaluates roughness, porosity, and uniformity.
Sterilization: Implants are packaged and sterilized to ensure safe surgical use.
Titanium vs. Other Implant Materials
| Feature | Titanium Implant | Zirconia/Ceramic Implant |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal (Titanium) | White ceramic (Zirconia) |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent | High, especially for metal-sensitive patients |
| Aesthetic Outcome | Requires crown for color match | Naturally white, seamless appearance |
| Strength and Durability | Superior, high fracture resistance | Strong but more brittle than titanium |
| Bone Integration | Rapid and predictable | Excellent but slightly slower in some cases |
| Ideal Use | Full arch, posterior teeth, single teeth | Anterior teeth, aesthetic zones |
Titanium remains the preferred material for long-term durability and versatility, while zirconia implants are increasingly chosen for metal-free and highly aesthetic restorations.
The Titanium Implant Procedure
1. Pre-Surgical Assessment
Prior to placement, a thorough evaluation is conducted:
Oral Examination: Assessment of gum health, bite alignment, and jawbone quality.
Radiographic Imaging: CBCT scans and panoramic X-rays determine bone volume, density, and anatomical landmarks.
Medical Review: Identification of systemic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or osteoporosis.
Treatment Planning: Selection of implant type, size, and placement position for optimal prosthetic outcome.
2. Surgical Placement
The surgical procedure includes:
Anesthesia or Sedation: Ensures patient comfort.
Incision of Gum Tissue: Provides access to the jawbone.
Osteotomy Preparation: Drilling precise holes to accommodate the implant.
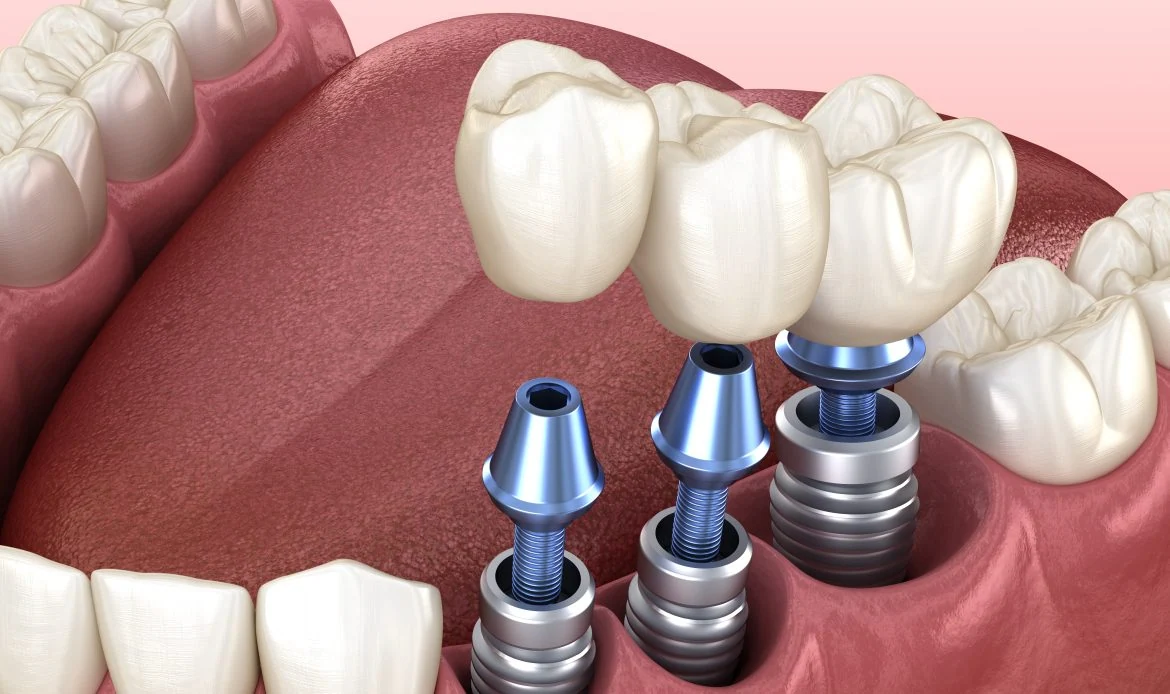
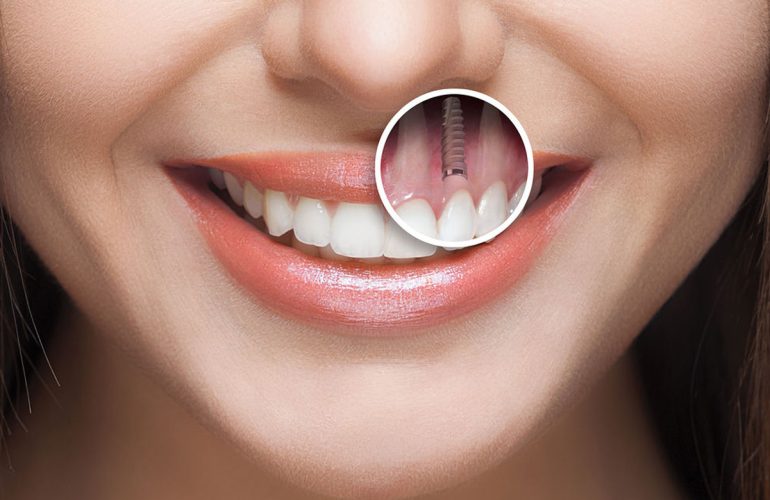
Implant Insertion: Titanium implants are placed with high primary stability, critical for successful osseointegration.
Suturing and Healing: The gum is closed, allowing the implant to heal undisturbed.
3. Healing and Osseointegration
Titanium implants fuse with the jawbone over 3 to 6 months, creating a stable foundation for prosthetic crowns or bridges. During this period:
Temporary prosthetics may be used.
Patients should maintain excellent oral hygiene and follow post-operative care instructions.
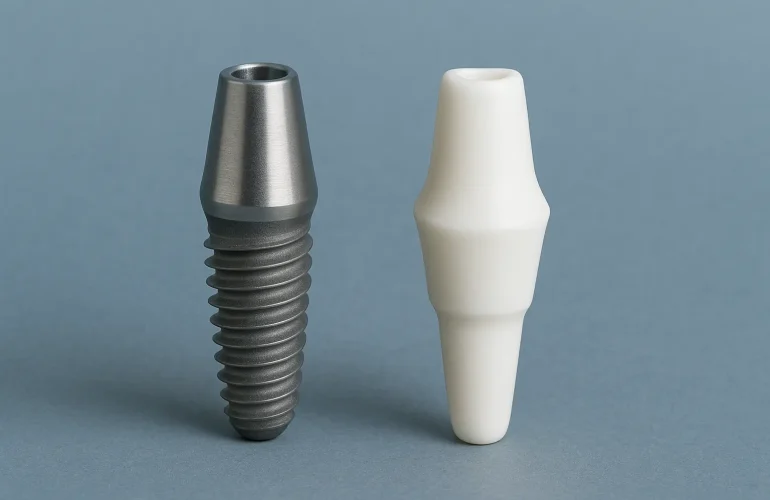
4. Abutment and Crown Placement
Abutment Connection: Attaches the implant to the final prosthetic restoration.
Crown Fabrication: Custom ceramic or zirconia crowns are created to match natural teeth in color, shape, and translucency.
Final Restoration: Provides full functionality, aesthetics, and bite alignment.
Post-Operative Care for Titanium Implants
Maintaining titanium implants requires:
Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and antiseptic rinses.
Dietary Considerations: Soft diet during initial healing, gradually returning to normal foods.
Routine Check-Ups: Monitor implant stability, gum health, and bone integration.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol to promote optimal healing.
Clinical Considerations and Success Factors
Titanium implants demonstrate high success rates due to:
High Mechanical Strength: Resistant to fracture under normal function.
Predictable Bone Integration: Strong osseointegration reduces implant failure.
Versatility in Prosthetic Design: Can support single crowns, bridges, or full-arch restorations.
Longevity: Studies show titanium implants maintain function and aesthetics for 20+ years with proper care.
Titanium dental implants remain the benchmark for modern restorative dentistry, offering unmatched strength, durability, and clinical predictability. Through advanced manufacturing, surface treatments, and precise surgical placement, titanium implants provide patients with reliable, natural-looking tooth replacements. With proper assessment, surgical technique, and post-operative care, titanium implants ensure long-term oral health, functional stability, and enhanced quality of life, making them the preferred choice for patients seeking highly successful and lasting dental restorations.