Maintaining healthy gums is a crucial part of overall oral health. While teeth often take the spotlight in dental care, gum problems can be equally, if not more, damaging if left untreated. Healthy gums support teeth, protect the jawbone, and play a vital role in preventing infections. When gum problems are ignored, they can lead to severe conditions such as periodontitis, tooth loss, and even systemic health complications.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the causes of gum problems, early signs to watch for, treatment options, and preventive measures to ensure long-lasting oral health.
Common Causes of Gum Problems
Gum problems are often the result of poor oral hygiene, but other lifestyle and health factors can contribute. Understanding the root causes is the first step toward effective prevention and treatment.
1. Plaque and Tartar Buildup
The most common cause of gum problems is plaque—a sticky, bacteria-filled film that forms on teeth. If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar (calculus), which irritates the gums and leads to inflammation.
2. Poor Oral Hygiene
Infrequent brushing, not flossing daily, and skipping dental checkups allow bacteria to thrive. Over time, this neglect causes gingivitis and, if untreated, more advanced gum disease.
3. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, puberty, menopause, and monthly menstrual cycles can make gums more sensitive and vulnerable to gum infections.
4. Tobacco Use
Smoking or chewing tobacco weakens the immune system, reduces gum tissue healing, and accelerates gum disease progression.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain diseases, such as diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders, increase the risk of gum problems. Medications that cause dry mouth also contribute to gum issues.
6. Nutritional Deficiencies
Lack of vitamin C, vitamin D, and calcium can weaken gum tissue, making it more susceptible to infections and bleeding.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Gum Problems
Recognizing gum problems early ensures timely treatment and prevents complications. Common symptoms include:
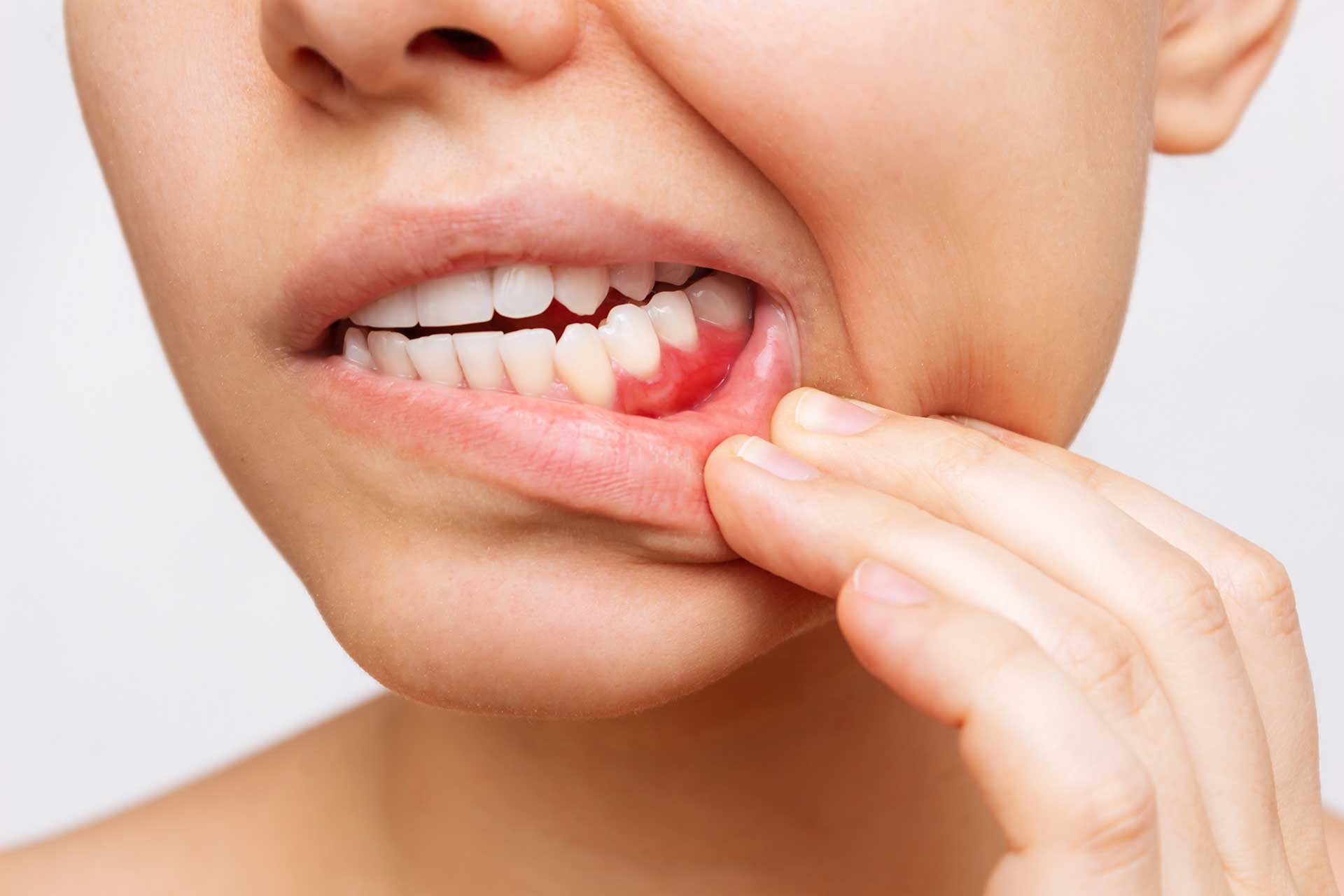
Red, swollen, or tender gums
Bleeding while brushing or flossing
Receding gum line (teeth appear longer)
Persistent bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
Loose or shifting teeth
Pus between teeth and gums
If these symptoms are ignored, gum disease can progress from gingivitis (early stage) to periodontitis (advanced stage).
Types of Gum Problems
Not all gum problems are the same. Understanding the types helps in seeking proper treatment.
1. Gingivitis
Mildest form of gum disease
Caused by plaque buildup
Symptoms: red, swollen gums that bleed easily
Reversible with proper oral care
2. Periodontitis
Advanced gum disease
Occurs when gingivitis is untreated
Symptoms: gum recession, bone loss, loose teeth
Requires professional treatment such as scaling, root planing, or surgery
3. Gum Recession
Gums pull away from teeth, exposing roots
Increases sensitivity and risk of tooth decay
Commonly caused by aggressive brushing, gum disease, or genetics
4. Gum Abscess (Periodontal Abscess)
Painful infection caused by bacterial buildup
Symptoms: swelling, pus discharge, throbbing pain
Requires immediate dental treatment
Treatment Options for Gum Problems
Effective treatment depends on the severity of gum issues.
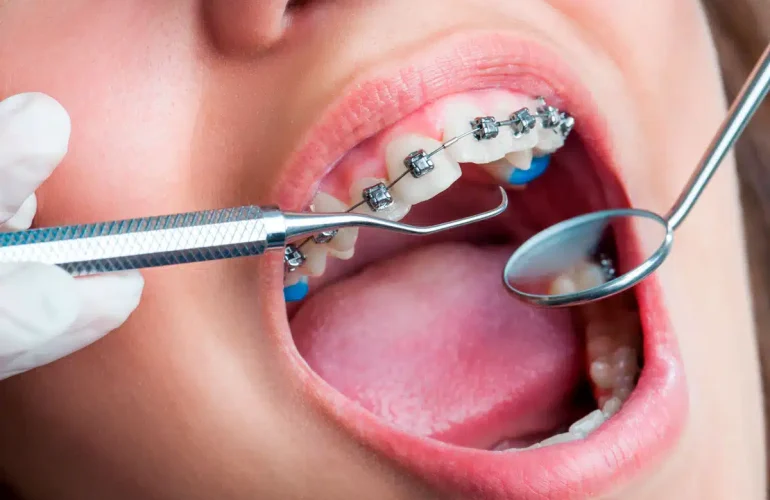
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
Dentists remove plaque and tartar buildup through scaling and polishing. Regular cleanings prevent early gum disease from progressing.
2. Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
For patients with periodontitis, dentists perform deep cleaning below the gum line to smooth root surfaces and remove bacteria.
3. Antibiotic Therapy
Oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce gum infections.
4. Surgical Treatments
Flap surgery: Gums are lifted back to remove tartar from deep pockets.
Bone grafting: Restores bone loss due to gum disease.
Gum grafting: Repairs gum recession and protects exposed roots.
5. Laser Therapy
Minimally invasive option that removes infected tissue and promotes healing.
Home Remedies and Daily Care
While professional treatment is necessary for advanced cases, home care plays a vital role in managing and preventing gum problems.
Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
Use an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria
Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
Quit smoking and reduce alcohol intake
Stay hydrated to prevent dry mouth
Prevention of Gum Problems
The best way to combat gum problems is prevention. Here are essential steps for lifelong gum health:
Visit your dentist every 6 months for professional cleaning and checkups.
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid damaging gum tissue.
Replace toothbrush every 3–4 months.
Manage systemic health conditions like diabetes to lower risk.
Be aware of family history, as genetics can influence gum health.
Complications of Untreated Gum Problems
Ignoring gum problems can have severe consequences not only for oral health but also for overall health:
Tooth loss due to bone destruction
Chronic bad breath
Increased risk of heart disease and stroke
Diabetes complications
Weakened immune system response
When to See a Dentist
We recommend seeking immediate dental consultation if you notice:
Continuous gum bleeding
Persistent bad breath despite oral hygiene
Painful swelling or pus discharge
Loose teeth or sudden shifting in bite
Early diagnosis ensures treatment is less invasive and more effective.
Healthy gums are the foundation of a strong smile and overall wellness. Addressing gum problems early with proper dental care, lifestyle adjustments, and professional treatments ensures long-term oral health. Regular dental visits, consistent oral hygiene practices, and healthy lifestyle choices are the key to preventing gum disease and preserving your natural teeth for life.